What is ear wax?
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the glands in the ear canal. It plays an essential role in maintaining the health of the ear by protecting and lubricating the ear canal, as well as trapping dust, dirt, and other foreign particles (dust, insects etc) to prevent them from entering and damaging the eardrum. Also, as its waxy in nature, it repels water and moist keeping the ear canal and the ear drum free from excess water/moist.
Ear wax typically consists of a combination of secretions from glands in the ear canal, along with dead skin cells and hair lining the ear canal and dirt of course! It varies in colour and consistency among individuals, ranging from yellow to brown and being either wet or dry/scally.
The ear naturally expels excess ear wax, often through jaw movements while talking or chewing. However, some individuals may produce more wax than can be easily expelled, leading to a buildup of ear wax or blockage in the ear canal. Also, in certain individuals, the wax can be dry and hard to expel out. This buildup can sometimes cause hearing problems, discomfort, or a feeling of fullness in the ear.
How do I know if I need ear wax removal?
There are several signs that may indicate you need ear wax removal:
Ear Discomfort
If you’re experiencing ear pain or discomfort, it could be due to an accumulation of ear wax. This may feel like a fullness or pressure in the ear.
Hearing Problems
A buildup of ear wax can obstruct the ear canal, leading to reduced hearing or even temporary hearing loss. Sounds might seem muffled or unclear.
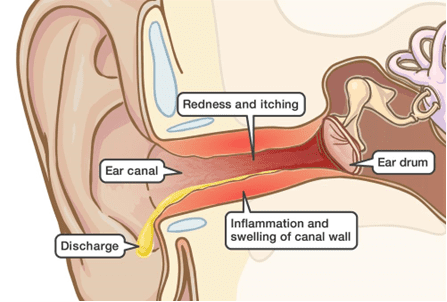
Ear Itching or Discharge
Excessive ear wax can sometimes cause itching inside the ear due to irritation of the skin or a discharge, which might be tinged with blood due to minor abrasions caused by scratching.
Ear wax impaction can also contribute to earaches or ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
Dizziness or Coughing
In rare cases, if ear wax builds up significantly and presses against the eardrum, it might lead to symptoms like dizziness (unsteadiness) or coughing.
If you experience any of these symptoms and suspect that ear wax might be the cause, it’s important not to try removing it yourself using cotton swabs, bobby pins, or any other objects, as this can push the wax further into the ear canal and potentially cause damage or injury.
Instead, consult a healthcare professional such as an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist, audiologist, or a doctor. They can examine your ears using specialized tools and safely remove the excess ear wax using methods like irrigation, suction, or manual removal with instruments designed for this purpose.
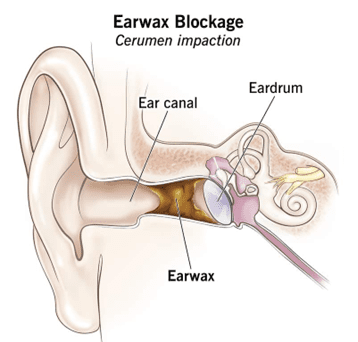
Reasons why ears get blocked
Ears can become blocked or feel plugged due to various reasons, including:
Ear Wax Buildup
Excessive accumulation of ear wax can block the ear canal, leading to a feeling of fullness or hearing loss.
Living and/or working environment can be dusty and humid causing ear wax to buildup.
Ear Infections
Infections, such as middle ear infection or ear canal (swimmer’s ear), can cause inflammation and fluid buildup, leading to a feeling of blockage or pressure in the ear.
Fluid Accumulation
Fluid accumulation in the middle ear due to allergies, sinus infections, or changes in air pressure (as during air travel, bungie jumping) can cause a sense of fullness or blockage.
Foreign Objects
Objects inserted into the ear, even inadvertently (e.g., cotton swabs), can push wax further into the ear canal or cause an obstruction.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, helps regulate pressure in the ear. Dysfunction in this tube, often due to colds, allergies, or sinus infections, can cause a blocked sensation. Also, the shape of the ear canal can cause wax retention.
Barotrauma
Sudden changes in air pressure, such as when flying, scuba diving, or driving in high altitudes, can temporarily block the ears. This sensation usually resolves as the pressure equalizes.
Tumours or Growths
Rarely, tumours or abnormal growths in the ear canal can cause a feeling of blockage or fullness in the ear.
Earphones, hearing aids and ear plugs are very common objects causing impairment of natural drainage of ear wax causing impaction. Also, constant stimulation of the lining of the ear canal causes the accumulation of wax too.
If you experience persistent or severe ear blockage, discomfort, pain, or a significant decrease in hearing, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Avoid attempting to remove blockages yourself, especially using objects like cotton swabs, as this can worsen the problem or cause unexpected injury.
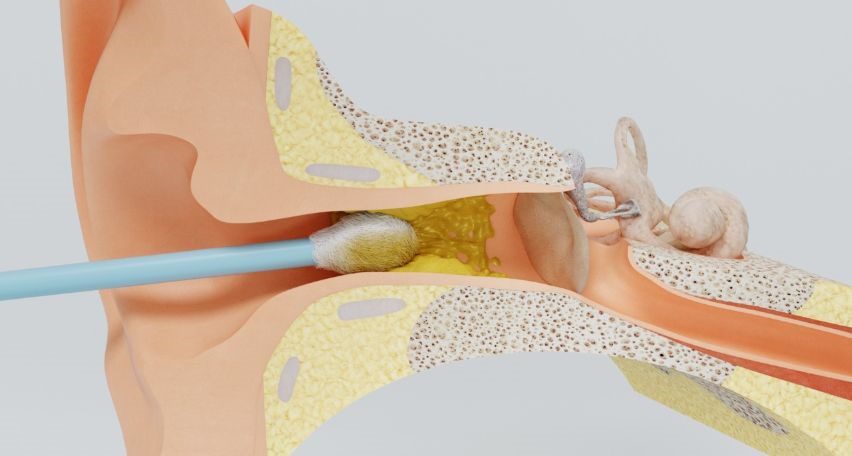
The risk of ear wax buildup
Ear wax buildup, also known as impacted ear wax, can pose several risks and complications if left untreated:
Hearing Impairment
Excessive accumulation of ear wax can block the ear canal, leading to reduced hearing or even temporary hearing loss. Sounds may become muffled or unclear or might sound coming for a far distance.
Ear Pain and Discomfort
Impacted ear wax can cause discomfort, pain, or a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
Ear Infections
Buildup of wax can create a conducive environment for bacterial growth, increasing the risk of ear infections such as external ear infections (swimmer’s ear) or middle ear infections. Attempts to remove can cause further damage.
Sometimes, impacted ear wax can contribute to ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears (tinnitus).
Vertigo and Dizziness
In severe cases, pressure from impacted ear wax against the eardrum might lead to symptoms of dizziness or vertigo.
Impaired Cleaning Mechanism
Ear wax naturally helps clean and protect the ear canal. Excessive removal or blockage can interfere with this self-cleaning mechanism, potentially leading to further wax buildup or dryness. This, of course, is one of the well-known factors of wax impaction even though you and I do not realise!
Difficulty in Ear Examination
If a healthcare professional needs to examine your ears for other conditions or issues, impacted ear wax might hinder their ability to do so accurately.
To prevent the risks associated with ear wax buildup, it’s essential to avoid inserting objects into the ear canal to remove wax (cotton buds/bobby pins/plastic rods etc). Instead, if you experience symptoms of excessive ear wax or feel a blockage in your ears, seek guidance from a healthcare professional. They can safely assess your ears using recommended instruments and, if necessary, use appropriate methods to remove the excess wax without causing harm or further complications. Regular ear hygiene and maintenance can also help prevent significant wax accumulation.
Methods of ear wax removal
There are several safe and effective methods for ear wax removal that healthcare professionals may use based on the amount of ear wax buildup and the individual’s specific situation. Some common methods include:
Ear Irrigation or Syringing
This procedure involves flushing the ear canal with a gentle flow of warm water to dislodge and remove the excess ear wax. It’s typically done using a specialized syringe or irrigation device under controlled pressure. Ear irrigation should be performed by a healthcare professional to avoid injury to the ear.
Manual Removal
A healthcare provider may use specialized instruments like a curette or suction device to carefully extract the impacted ear wax. This method requires expertise and should only be performed by trained professionals to prevent injury to the ear canal or eardrum.
Ear Drops
Over-the-counter or prescription ear drops can help soften and loosen ear wax, making it easier to remove. These drops often contain ingredients like mineral oil, hydrogen peroxide, glycerin, or carbamide peroxide. Following the instructions provided by a healthcare professional is crucial for safe and effective use of ear drops.
Micro-suction
This method involves using a suction device, usually with a microscope or magnifying lens, to gently suction out the ear wax. It’s a precise and effective way to remove impacted ear wax and is commonly performed by ENT specialists but can be performed by a trained doctor or registered nurse. An inexperienced hand can perforate the eardrum or can cause damage to the ear canal.
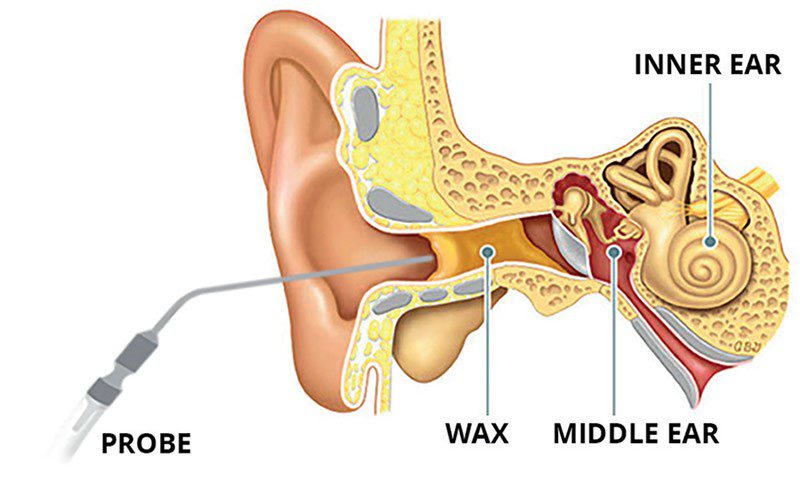
Cerumenolytics
These are medications or solutions specifically designed to dissolve or break down ear wax. They can be prescribed by a healthcare professional and are often used before other removal methods to soften the wax.
Out of all, Irrigation/syringing and Micro-suction followed by wax softeners are the most common and effective methods. It’s important to note that attempting to remove ear wax at home using cotton swabs, bobby pins, or other objects can push the wax deeper into the ear canal, leading to further blockage or injury. If you suspect excessive ear wax buildup or experience symptoms like hearing loss, discomfort, or ear blockage, it’s best to seek guidance from a healthcare professional, such as an ENT specialist or a doctor, for safe and effective ear wax removal.
What happens during an ear wax removal appointment?
During a wax removal appointment, a healthcare professional, often an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist, audiologist, or a doctor, will assess your ears and determine the most suitable method for removing the ear wax buildup. Here’s what typically happens during a wax removal appointment:
Evaluation
The healthcare provider will examine your ears using an otoscope or another specialized tool to assess the extent of the ear wax buildup and check for any signs of infection or other ear-related issues.
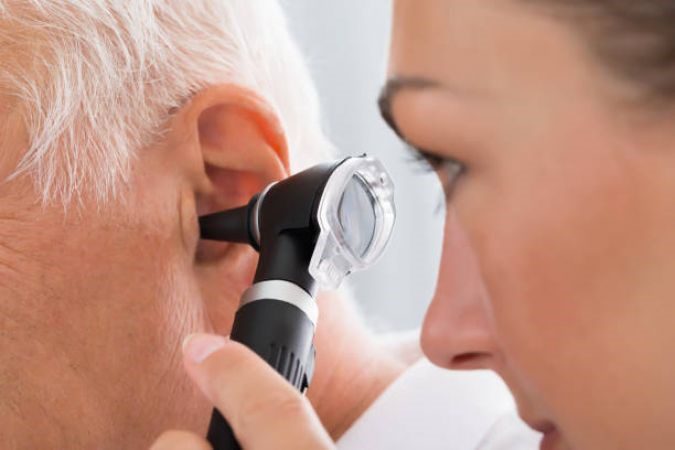
Discussion of Symptoms
They will inquire about any symptoms you’ve been experiencing, such as hearing loss, ear discomfort, tinnitus, or a feeling of fullness in the ears.
Explanation of Procedure
The healthcare professional will explain the procedure they plan to use for removing the ear wax and discuss any potential risks or discomfort you might experience during the process.
Ear Wax Removal
Depending on the situation, the healthcare provider will proceed with the appropriate method for ear wax removal, which could involve ear irrigation, manual removal using specialized instruments, micro-suction, or the use of ear drops to soften the wax.
Procedure Duration
The duration of the procedure can vary based on the amount of ear wax buildup and the chosen removal method. It might take a few minutes to complete, but it can vary from person to person.
Post-Procedure Advice
After the wax removal, the healthcare professional might provide you with instructions on how to care for your ears, such as avoiding further insertion of objects into the ear canal or using ear drops for a certain period to prevent future buildup.
Follow-Up
In some cases, a follow-up appointment might be recommended, especially if there’s a history of recurrent ear wax problems or if there are underlying conditions contributing to the buildup.
It’s important to communicate any discomfort or concerns you may have during the procedure to the healthcare provider. They will prioritize your comfort and safety throughout the process. Additionally, following their post-procedure advice can help prevent excessive wax buildup and maintain healthy ears.
How to wash your ears at home?
Cleaning your ears at home should be done carefully to avoid damaging the ear canal or pushing wax deeper. Here’s a safe method for cleaning your ears:
Use a Washcloth
Gently clean the outer part of your ears (auricle) using a damp washcloth during your regular bath or shower routine. Avoid inserting the cloth or any objects into the ear canal.
Ear Irrigation
If you have a history of ear wax buildup you may perform this at home but, the cons would be more profound than the pros! There are plenty of devices that you can buy from pharmacies, however, there is always a risk of health hazards; therefore, we do not encourage this method as a home remedy.
Ear Drops
Over-the-counter ear drops specifically designed to soften ear wax can be used according to the instructions provided by your doctor or nurse or the pharmacist. These drops can help loosen ear wax, making it easier for the wax to move out of the ear naturally.
It’s important to note that inserting cotton swabs, Q-tips, bobby pins, or any other objects into your ear canal can push wax deeper and increase the risk of injury, infection, or impacted ear wax. The ear is self-cleaning and using these items can disrupt the natural process.
If you experience symptoms like hearing loss, discomfort, or a feeling of fullness in your ears, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional immediately, rather than attempting to remove the ear wax at home. They can safely assess your ears and perform necessary procedures to remove the excess wax without causing harm.
Appointment details
We offer ear cleaning services in Auckland. Ear cleaning is done by our nurses once been seen by a doctor and has used ear drops for 3 days to soften the ear wax. We do not do ear syringing on children.